New research "sniffs out" how associative memories are formed
UCI-led team is first to discover how the brain creates memories of delicious smells

Irvine, Calif., Sept. 22, 2021 — Has the scent of freshly baked chocolate chip cookies ever taken you back to afternoons at your grandmother’s house? Has an old song ever brought back memories of a first date? The ability to remember relationships between unrelated items (an odor and a location, a song and an event) is known as associative memory.
Psychologists began studying associative memory in the 1800s, with William James describing the phenomenon in his 1890 classic The Principles of Psychology. Scientists today agree that the structures responsible for the formation of associative memory are found in the medial temporal lobe, or the famous “memory center” of the brain, but the particular cells involved, and how those cells are controlled, have remained a mystery until now.
Neuroscientists at the University of California, Irvine have discovered specific types of neurons within the memory center of the brain that are responsible for acquiring new associative memories. Additionally, they have discovered how these associative memory neurons are controlled. We rely on associative memories in our everyday lives and this research is an important step in understanding the detailed mechanism of how these types of memories are formed in the brain.
“Although associative memory is one of the most basic forms of memory in our everyday life, mechanisms underlying associative memory remain unclear” said lead researcher Kei Igarashi, faculty fellow of the Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory and assistant professor of anatomy & neurobiology at the UCI School of Medicine.
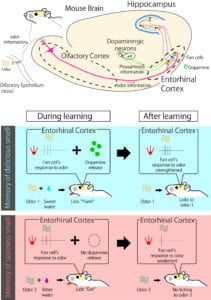
The study published today in the journal Nature reports for the first time that specific cells in the lateral entorhinal cortex of the medial temporal lobe, called fan cells, are required for the acquisition of new associative memories and that these cells are controlled by dopamine, a brain chemical known to be involved in our experience of pleasure or reward.
In the study, researchers used electrophysiological recordings and optogenetics to record and control activity from fan cells in mice as they learn to associate specific odors with rewards. This approach led researchers to discover that fan cells compute and represent the association of the two new unrelated items (odor and reward). These fan cells are required for successful acquisition of new associative memories. Without these cells, pre-learned associations can be retrieved, but the new associations cannot be acquired. Additionally acquiring new associations also requires dopamine.
“We never expected that dopamine is involved in the memory circuit. However, when the evidence accumulated, it gradually became clear that dopamine is involved,” said Igarashi. “These experiments were like a detective story for us, and we are excited about the results.”
This discovery is an important piece in the puzzle of understanding how memories are formed in the brain and lays a foundation on which other researchers can continue to build. Associative memory abilities are known to decline in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s Disease. Understanding the neurobiological mechanism of how these memories are formed is the first step to developing therapeutics to slow the loss of associative memory abilities in Alzheimer’s Disease.
The research team also included Jason Y. Lee, Heechul Jun, Shogo Soma, Tomoaki Nakazono, Kaori Shiraiwa, Ananya Dasgupta, Tatsuki Nakagawa, Jiayun L. Xie, Jasmine Chavez, Rodrigo Romo and Sandra Yungblut with UCI’s Department of Anatomy & Neurobiology; and Meiko Hagihara and Koshi Murata, division of brain structure and function, University of Fukui, Japan.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Health (award numbers R01MH121736, R01AG063864, R01AG066806), a PRESTO grant from Japan Science and Technology Agency (JPMJPR1681), a Brain Research Foundation Fay-Frank Seed Grant (BRFSG-2017-04), a Whitehall Foundation Research Grant (2017-08-01), a BrightFocus Foundation Research grant (A2019380S), an Alzheimer’s Association Research Grant (AARG-17-532932) and a New Vision Research Investigator Award (CCAD201902) to Kei Igarashi. Heechul Jun was supported by the University of California, Irvine Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) (T32GM008620) and an NIH F31 grant (1F31AG069500).
About the Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory: Established in 1983 by the UC Regents, with James L. McGaugh as its Founding Director, the CNLM is the first research institute in the world dedicated to the interdisciplinary study of the fundamental brain mechanisms of learning and memory. It is credited with numerous seminal discoveries about how memory works and is recognized as a global leader in the area. Led by Director Michael Yassa, the CNLM is home to more than 120 faculty scientists at UCI and beyond. The Center has also developed a number of successful training programs for neuroscience education at all levels and is deeply committed to enhancing diversity and inclusion in academia. For more information on the CNLM, visit cnlm.uci.edu.
About the Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology: Established in 1968, the Department of Anatomy & Neurobiology at the UC Irvine School of Medicine is a world-leading neuroscience department under the directorship of Chair Christine Gall, where discoveries at the molecular, anatomical and physiological levels are seamlessly integrated to the development of new treatments for neurological diseases. https://www.anatomy.uci.edu/
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UCI is the youngest member of the prestigious Association of American Universities and is ranked among the nation’s top 10 public universities by U.S. News & World Report. The campus has produced three Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UCI has more than 36,000 students and offers 224 degree programs. It’s located in one of the world’s safest and most economically vibrant communities and is Orange County’s second-largest employer, contributing $7 billion annually to the local economy and $8 billion statewide. For more on UCI, visit www.uci.edu.
Media access: Radio programs/stations may, for a fee, use an on-campus ISDN line to interview UCI faculty and experts, subject to availability and university approval. For more UCI news, visit wp.communications.uci.edu. Additional resources for journalists may be found at communications.uci.edu/for-journalists.